The Opening Stage Is The First Stage Of Childbirth

Childbirth is divided into three phases, which are the opening phase, the effort phase, and the exit of the offspring. Today, we will focus on the first of these steps, the opening phase.
The cervix plays a key role during the opening phase. The contractions allow it to open and thus the baby to be born. In the case of premature contractions, the cervix may shorten or open considerably. In this case, it is recommended to go to the hospital to stop the contractions and check the condition of the mother and fetus. However, during pregnancy, the cervix stays normally closed to keep the fetus warm and safe during its development.
The opening phase begins when regular contractions that open the cervix begin and ends when the cervix opens completely. During this stage, the cervix softens and disappears and the baby’s tender part settles to the bottom of the mother’s pelvis.
How does the opening phase start?
The opening phase can be started in two ways:
- Naturally and spontaneously without the need for medical help.
- Medications in cases where initiation of labor is considered necessary for maternal or fetal health.
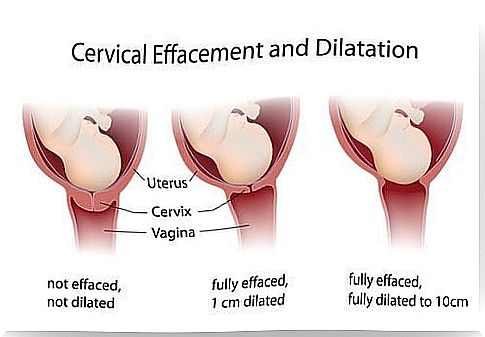
Progress of the opening phase
The opening phase is the phase that begins with the onset of contractions and ends with the onset of the effort phase. It is the longest stage of childbirth that can last for hours. In first-time mothers, the opening phase typically takes 7-14 hours and in others 6-10 hours.
The cervix opens an average of one centimeter per hour, but the rate of opening is not regular. The first centimeters usually take the most time. But this, of course, is just an average situation, as every mother is different, just like every childbirth.
The opening phase is divided into three phases, which we list below.
1. Latency phase
Contractions occur every 5 to 30 minutes and typically last 30 to 45 seconds. Mild contractions can be felt as pain in the back and groin. Even mild contractions do their job, and at this point the cervix can open up to three centimeters.
2. Active opening phase
At this point, contractions first occur every 5 minutes and last for 30-40 seconds. The cervix opens up to 5 centimeters.
Next, contractions begin to occur every 2-3 minutes and can last for 50 seconds. The cervix opens to six centimeters.
3. Acceleration phase
This is the last stage of cervical opening, in which the opening has progressed to 10 centimeters. At this point, the process speeds up, and contractions occur every 2-3 minutes, and they last longer, leaving the woman with little time to rest.
The mother may also experience nausea, vomiting, hot flashes, or chills at this point. This is the most difficult stage of childbirth for a woman.
Types of opening
Passive opening
The cervix opens 0-3 cm and the contractions appear irregularly and are moderately strong.
It is then useful for the mother to be at home or in a quiet environment. He should not go to the hospital until contractions come every five minutes for an hour.
Active opening
The cervix opens to 3-10 centimeters and the contractions become denser and stronger.
In this situation, it is best to be in the hospital, as such contractions predict that the baby will soon be on its way.

When cervical opening does not progress
Sometimes the opening of the cervix does not happen fast enough or even stops.
Reasons for this may include: an abnormal cervix, the mother’s previous surgical procedures on the cervical area, a baby that is too big for the mother’s pelvis, or contractions that are not very effective.
But this does not mean, however, that caesarean section is inevitable. Hospital nursing staff may be able to resolve the situation with some other technical aids.
- The amniotic membranes can be punctured. This procedure usually results in stronger contractions as well as greater pressure on the baby’s head caused by the cervix.
- Synthetic oxytocin injection. This hormone acts in addition to the natural oxytocin produced by uterine contractions and helps intensify contractions and make them denser.